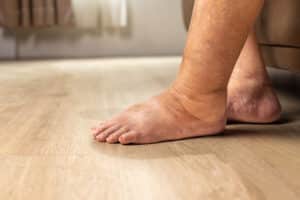
Lymphoedema of the legs
Lymphatic drainage for lymphoedema of the legs: causes, symptoms, treatment and the five most important self-help tips
Lymphoedema in the legs is a major challenge in everyday life for many people. The typical swelling and feeling of tightness not only affect freedom of movement, but also general well-being. The manuel lymphatic drainage is a proven physiotherapeutic method that specifically helps to relieve pain and improve freedom of movement. But what exactly is lymphoedema, how does it develop and how can lymphatic drainage help? This article gives you a comprehensive overview of the causes, symptoms and treatment options as well as five practical tips for self-help.
What is lymphoedema?
Lymphoedema is a chronic swelling that occurs when the lymphatic system - an important part of the immune system - can no longer adequately remove excess tissue fluid. This accumulation of fluid leads to visible swelling, which is usually painless, but over time can restrict freedom of movement and increase the risk of infection.
There are two main forms:
- Primary lymphedema: Primary lymphoedema is congenital and is caused by malformations or underdevelopment of the lymph vessels. The swelling often occurs at a young age, usually starts on the toes or the back of the foot and can spread to the entire leg. This form can affect people of all genders, often without any recognizable triggers.
- Secondary lymphedema:Secondary lymphoedema develops as a result of damage to or blockage of the lymph channels. Common causes are operations, injuries, radiation or infections. This form is particularly common after cancer treatment where lymph nodes have been removed. Chronic venous disease or repeated inflammation can also cause secondary lymphoedema.
lymphatic drainage physiotherapy Wipkingen
Typical symptoms of lymphoedema
The symptoms of lymphoedema often develop gradually and are easily overlooked at first. The most common signs include
- Visible, usually painless swelling of the foot, ankle or leg
- Feeling of tension and heaviness in the legs
- Limited freedom of movement and stiffness
- Skin changes such as thickening, hardening or a shiny surface
- In advanced stages: recurrent infections, wound healing disorders or cracks in the skin
These symptoms not only impair mobility, but can also increase the risk of complications such as erysipelas.
The role of lymphatic drainage in physiotherapy
Manual lymphatic drainage is a special massage technique performed by experienced physiotherapists. The aim is to specifically promote the drainage of lymphatic fluid and thus reduce swelling. Gentle, rhythmic movements along the lymph channels move the fluid in the direction of the lymph nodes. The treatment is painless and is individually adapted to the needs of the person concerned.
Scientific studies prove, that lymphatic drainage - especially in combination with compression therapy and targeted exercise training - significantly improves the quality of life of people with lymphoedema. It not only helps to reduce swelling, but also increases freedom of movement, relieves the feeling of heaviness in the legs and reduces the risk of infection. The therapy can be used both in the acute stage and to maintain freedom of movement in the long term.
Who benefits from lymphatic drainage?
Lymphatic drainage is particularly suitable for people with:
- Primary or secondary lymphoedema of the legs
- Swelling after operations or injuries
- Chronic venous insufficiencies
- Complaints after tumor treatment
Athletes, pregnant women and older people with limited mobility can also benefit from this lymph therapy. The treatment is individually tailored to the respective situation and can be used for both short-term pain relief and long-term prevention.
Five proven tips for self-help with lymphoedema
- Regular exerciseActivate your lymphatic system with light exercise such as walking, cycling or swimming. These activities strengthen the muscle pump and promote fluid drainage. Avoid sitting or standing for long periods and integrate regular exercise breaks into your daily routine. Small exercises such as circling your feet or lifting your toes can also help to stimulate lymph flow.
- Consistent compressionWear correctly fitted compression stockings every day. They support the return flow of lymphatic fluid and prevent the swelling from worsening. Wearing compression stockings is particularly important during longer activities or when travelling to minimize the risk of deterioration.
- Leg positioningElevate your legs several times a day, ideally with your feet above heart level. This facilitates the return flow of fluid and noticeably relieves the tissue. Try to keep your legs slightly elevated while resting or sleeping. Even short breaks with your legs elevated can make a big difference.
- Careful skin careTake care of your skin with mild, moisturizing creams and pay attention to minor injuries. A healthy skin barrier protects against infections such as erysipelas. Avoid aggressive soaps and make sure you gently dry your skin after washing. Check the skin regularly for changes or small cracks.
- Breathing exercises and relaxationDeep abdominal breathing also stimulates the lymph flow. Take time several times a day for conscious breathing exercises and short relaxation phases. Reducing stress not only supports your immune system, but also promotes the healing process. Breathing exercises can be easily integrated into everyday life and can help to improve your general well-being.
The importance of prevention and rehabilitation
Early diagnosis and targeted treatment are crucial in order to avoid consequential damage and maintain quality of life. Preventive measures such as regular exercise, a healthy diet and avoiding obesity can reduce the risk of developing lymphoedema. As part of rehabilitation, physiotherapy not only helps to relieve pain, but also to restore freedom of movement and promote an active lifestyle.
Cooperation with medical specialists and the individual adaptation of the therapy are key components for successful treatment. Modern physiotherapeutic approaches rely on a combination of manual lymphatic drainage, compression, exercise and education of the affected person. This ensures that the therapy is optimally tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion
Lymphoedema in the legs can be a challenge, but with targeted physiotherapy, manual lymphatic drainage and consistent self-help, you can maintain your freedom of movement and improve your quality of life in the long term. Early diagnosis and individually tailored therapy are crucial for successful treatment. Take advantage of the possibilities offered by modern physiotherapy and get actively involved in your health - and regain your quality of life and mobility.
Categories
- Osteoarthritis
- Leg
- Extensions
- Dry needling
- Elbow
- Foot
- Balance
- Hand
- Hip
- Pine
- Knee
- Headache
- Lymphatic drainage
- Mobilization
- Muscle pain
- Myofascial therapy
- Neck pain
- Physiotherapy Höngg
- Physiotherapy Wipkingen
- Physiotherapy Zurich
- Rehabilitation
- Back pain
- Shoulder arm
- Shoulder pain
- Pregnancy
- Dizziness
- Sports
- Trigger points
- Exercises
- Lower leg
- Injury prevention
- Wade
- What to do?
- Wound healing
Neuro-focused training in physiotherapy
What is neuroathletic training (NAT)? Neuroathletic training (NAT) is a modern and holistic therapeutic approach...
Read articleAfter the cruciate ligament rupture: The way back to sport in Zurich
Your way back to sport after a cruciate ligament rupture A wrong step, an abrupt turn, a cracking sound...
Read articleSki preparation Zurich: Neuro-focused training for safe performance on the slopes
Ski preparation Zurich: Neuro-focused training for safe performance on the slopes at Physio Waidfuss The first snow...
Read articlePhysiotherapy for seniors Zurich Wipkingen
Movement is life - even at 60+ Growing older brings with it many positive aspects: more time for family and...
Read articleKnee injury after accident what to do?
After the accident: How physiotherapy helps with knee and leg injuries in Zurich Wipkingen The way back to full fitness is...
Read articlePut an end to office back pain in Zurich Wipkingen
Put an end to office back pain Do you know what it's like? A long working day, lots of screen time - your neck gets...
Read articleLymphoedema of the legs
Lymphatic drainage for lymphoedema of the legs: causes, symptoms, treatment and the five most important self-help tips Lymphoedema...
Read articleHamstrings injuries
Hamstring injuries: Prevention, symptoms and rehabilitation of hamstring injuries The hamstrings - also...
Read article