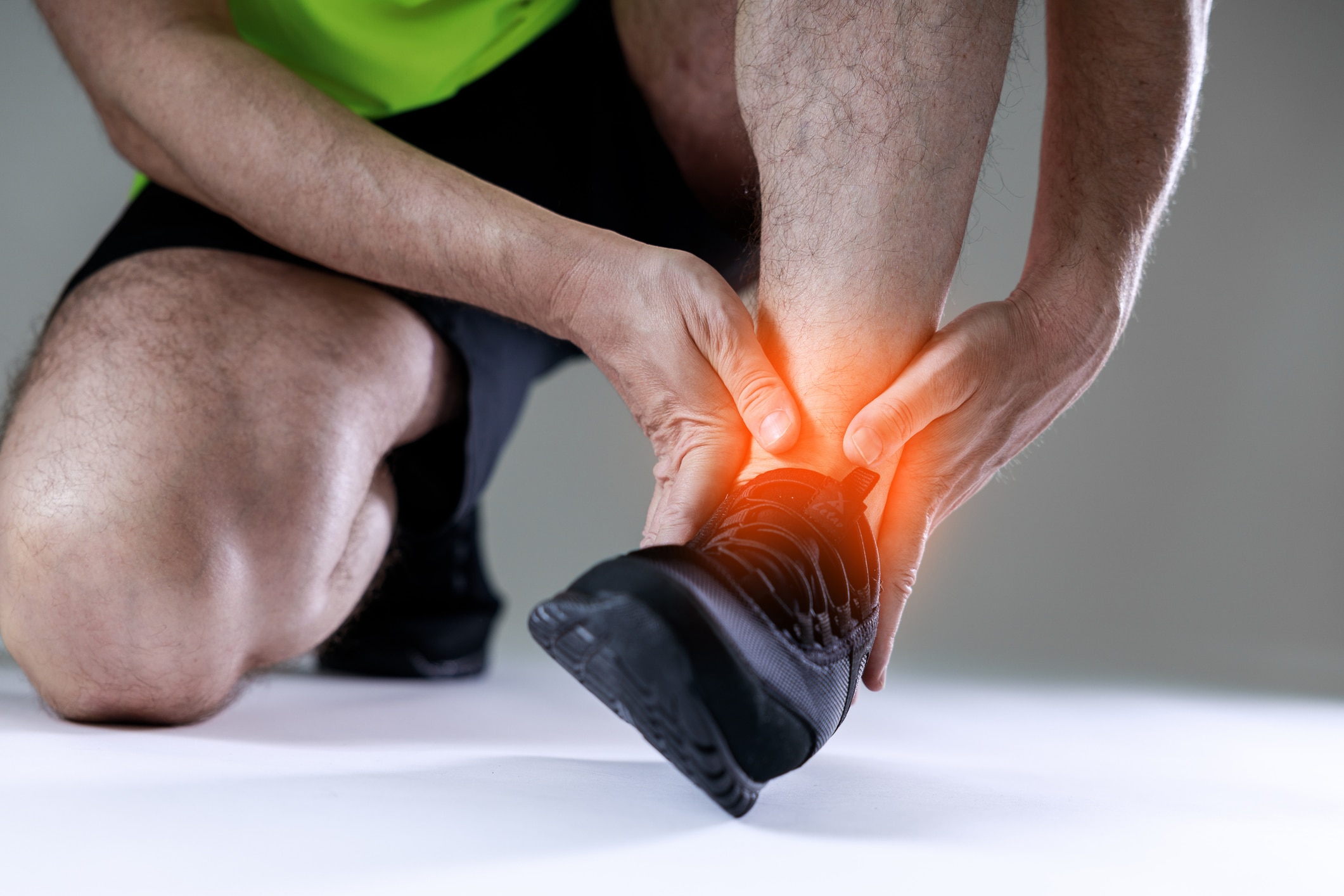
Sprained foot
Holistic treatment of ankle sprains: Effectively treating sprains of the foot
Ankle sprains, often referred to as sprains, are one of the most common accidental injuries and are often caused by a careless step or tripping on uneven ground. These injuries occur quickly, whether during sport or in everyday life. In the case of a sprain, the ligaments in the ankle are overstretched or partially torn without a complete tear occurring. The outer ligament is particularly affected, especially in the event of an accident in which the foot twists outwards - a known supination trauma.
Symptoms and need to see a doctor
Typical symptoms when the foot is sprained are a sudden, stabbing pain in the ankle, accompanied by swelling and possible bruising. Mobility is often severely restricted and there may be pressure pain or unsteadiness when walking. Although a sprained foot often heals without complications, untreated or improperly healed ligament sprains can lead to long-term instability, which in turn increases the risk of twisting the ankle again. Medical advice should be sought in the event of persistent pain, severe swelling or restricted mobility. A precise diagnosis can be made using ultrasound or MRI in order to determine suitable treatment methods.
Comprehensive support through physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic approaches promote the natural healing of the body holistically and effectively:
- Restoration of the joint mechanics: If the foot is sprained, the function of the joints in the foot may be impaired. Unnoticed blockages in the tarsal or lower leg joints can cause long-term complaints that extend to the knee, hip or back.
- Detection and resolution of voltage patterns: A sprained foot often affects the entire body statics. Muscle tension and adaptations of the fascia can extend to the back or pelvis. Physiotherapy treats the myofascial system comprehensively. Techniques such as Trigger point therapy and Dry needling can specifically improve muscle function by relieving tension at sensitive points.
- Promotes lymph flow and tissue healing: Manual techniques improve blood circulation and the Lymphatic drainageThe use of the skin care products is crucial for reducing swelling and supporting tissue healing.
- Prevention of incorrect loading: After a sprain, the body often adapts unconsciously to avoid pain. Physiotherapy helps to recognize such altered gait patterns at an early stage and prevent incorrect loading.
Targeted regeneration and active support
In the acute phase of a sprain, cooling, elevation and immobilization of the affected area are essential. Treatment with physiotherapeutic measures and targeted exercises is crucial for recovery: it ensures that incorrect strain and movement restrictions are recognized and corrected in good time.
Individual support as required:
- Functional exercises: These activate and strengthen the injured areas in a targeted manner.
- Stability and balance exercises: These promote the restoration of joint resilience and create a stable basis for everyday activities.
- Individual guidance for everyday life, work and sport: The aim is to lead an active and pain-free life despite the injury.
Comprehensive physiotherapy treatment is aimed at pain relief and rapid recovery without long-term consequences. It strengthens ligaments and joints, prevents chronic instability and supports long-term recovery if the foot is sprained.
The mechanism of a distortion
A sprain occurs when a joint is strained beyond its normal range of motion, either by twisting or twisting. Bones are temporarily displaced from their normal position without dislocating completely. The joint capsule is overstretched and damaged; in more severe cases, the surrounding ligaments are also affected.
Risk factors for sprains
Lack of or insufficient warm-up, fatigue, lack of concentration and weak muscles are risk factors that significantly increase the likelihood of an accident and the risk of a sprain.
Symptoms and diagnosis of a sprain
Symptoms include severe pain, which increases with movement, and rapidly swelling. The extent of the symptoms depends on the severity of the sprain. Diagnosis begins in the doctor's surgery with an examination of the affected joint and mobility tests. Ultrasound examinations help to detect a torn ligament, while X-rays rule out bone fractures.
Treatment according to the PECH principle
Immediate treatment according to the PECH principle is crucial for effective first aid:
- Pause (P): Avoids further strain on the sprained foot.
- Ice (E): Cold compresses or ice packs to reduce swelling.
- Compression (C): A tight bandage stabilizes and helps to reduce swelling.
- Elevate (H): Promotes blood and lymph flow, which reduces swelling.
For more severe sprains, painkillers such as ibuprofen can provide relief, while herbal ointments have a supportive effect. Regardless of the severity, stabilization should be provided by compression bandages or supports.
Return to sporting activities
After a mild sprain, sporting activity should only be resumed once the swelling has gone down and the joint can move again without pain. Severe cases can take several weeks to fully recover before a return to sport is advisable. We will be happy to help you with this. You can book an appointment here.
When should you see a doctor?
Medical advice should be sought immediately in the event of severe pain, pronounced swelling or restricted mobility. An accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment are crucial for successful healing and to prevent future problems, enabling an active lifestyle without restrictions.
Categories
- Osteoarthritis
- Leg
- Extensions
- Dry needling
- Elbow
- Foot
- Balance
- Hand
- Hip
- Pine
- Knee
- Headache
- Lymphatic drainage
- Mobilization
- Muscle pain
- Myofascial therapy
- Neck pain
- Physiotherapy Höngg
- Physiotherapy Wipkingen
- Physiotherapy Zurich
- Rehabilitation
- Back pain
- Shoulder arm
- Shoulder pain
- Pregnancy
- Dizziness
- Sports
- Trigger points
- Exercises
- Lower leg
- Injury prevention
- Wade
- What to do?
- Wound healing
Neuro-focused training in physiotherapy
What is neuroathletic training (NAT)? Neuroathletic training (NAT) is a modern and holistic therapeutic approach...
Read moreAfter the cruciate ligament rupture: The way back to sport in Zurich
Your way back to sport after a cruciate ligament rupture A wrong step, an abrupt turn, a cracking sound...
Read moreSki preparation Zurich: Neuro-focused training for safe performance on the slopes
Ski preparation Zurich: Neuro-focused training for safe performance on the slopes at Physio Waidfuss The first snow...
Read morePhysiotherapy for seniors Zurich Wipkingen
Movement is life - even at 60+ Growing older brings with it many positive aspects: more time for family and...
Read more